Maldives Judiciary System
1.
Explain the structure of the Maldives judicial system.Maldives
judiciary system
The judiciary of
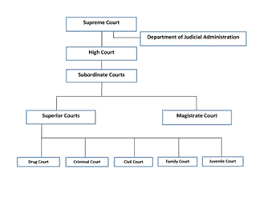
the Maldives is based on a three-tiered court system.
The courts of first instance include the Civil, Criminal, Family and Juvenile
courts established in Male' and the magistrate courts of the islands.
COURTS
Supreme
Court:
The Supreme Court, as stipulated under Article 141 of the Constitution of the
Republic of Maldives is the highest authority for the administration of Justice
in the Maldives. The Supreme Court is headed by a Chief Justice who is head of
the Judiciary. Along with the Chief Justice, the Supreme Court consists of five
Judges. The Constitution requires Supreme Court rulings to be disposed of by an
uneven number of Judges sitting together in session. The Supreme Court is the
highest authority on the interpretation of the Constitution, the Law, or any
other matter dealt with by a court of law.
The High
Court: The
High Court of the Maldives was created on 5 October 1980. The High Court was
the only court of appeal and the highest authority for the administration of
justice in the Maldives until the establishment of the Supreme Court on 18
September 2008. Article 141 of the Constitution vests power in The High Court
all the powers to administer justice in the Maldives.
Civil Court:
The Civil Court has the jurisdiction to adjudicate on all civil matters except
for those that are being determined by the Family Court. The Civil Court of the
Maldives was established on 1 August 1997 after abolishing court numbers 2 and
4.
Criminal
Court: The Criminal Court adjudicates on all cases of criminal
offences in the Maldives. The court functions under 3 main sections namely; the
Trial Offences, Legal Offences, and Summary Judgment.
Family
Court: The Family Court adjudicates on all matters relating to
family life under the Family Law of the Maldives, which was implemented in
2001. In addition, the court performs marriages, registers marriages and
divorces, and arrange for the consent of the judicial guardian of the bride.
Juvenile
Court: The Juvenile Court of the Maldives was established on 1
August 1997 to look into all matters of juvenile delinquency in the country.
The court adjudicates on all juvenile delinquency matters of those who have not
yet attained the age of 18. Cases are filed to the Juvenile Court through the
Prosecutor General’s Office once the matter has been investigated by relevant
Government authorities.
Island
(Magistrate) Courts: The Island Courts have the jurisdiction over
all, civil, criminal, family and juvenile cases in that particular island
except for certain serious legal issues like drug trafficking and abuse,
terrorism, murder, political offences, and civil cases involving more than 5
Million Rufiyaa. By 17 July 1979 an Island Court was established in every
inhabited island of the Maldives. Each Island Court is appointed with a
Magistrate.

Comments
Post a Comment